Virginia Tech Dendrology
Virginia Tech Dendrology
whitebark pine Pinaceae Pinus
albicaulis Engelm.
![]()
![]() symbol: PIAL
symbol: PIAL
Leaf: Evergreen needles, short (1 to 3 inches long), rigid, fascicles of 5, clustered near the ends of branches, green to yellow-green, with indistinct lengthwise rows of stomatal bloom. Remain on tree for 4 to 8 years.
Flower: Species is monoecious; male cones are pinkish, turning yellow-brown in tight clusters; female cones are deep red to purple.
Fruit: Small woody cone (1 1/2 to 3 inches long), almost round; imbricate scales are thick, blunt, and pointed but unarmed; serotinous (remain on the tree for several years with ripened seeds inside); seeds are large and usually wingless.
Twig: Stout but very flexible, silvery-white to gray.
Bark: When young smooth and gray-white, later darkening and becoming scaly, rarely more than 1/2 inch thick; inner bark is reddish brown.
Form: Typically small (20 to 50 feet tall and 1 to 2 feet in diameter) and contorted by the wind and harsh growing conditions.
Looks like: limber pine
- Rocky Mountain bristlecone pine
- western white pine
- sugar pine
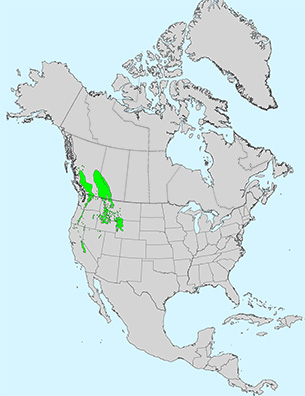
Additional Range Information: Pinus albicaulis is native to North America. Range may be expanded by planting. Download the full-size PDF map.
External Links: USDAFS Silvics of North America - USDAFS FEIS Silvics - USDA Plants Database
All material 2025 Virginia Tech Dept. of Forest Resources and Environmental Conservation; Photos and text by: John Seiler, Edward Jensen, Alex Niemiera, and John Peterson; Silvics reprinted from Ag Handbook 654; range map source information