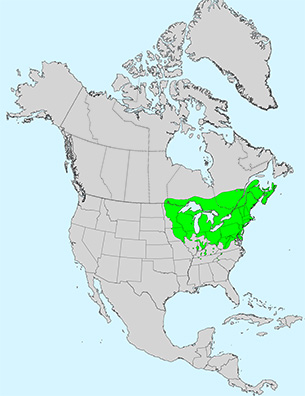



Bigtooth aspen is fast growing, short-lived tree, common to the northeastern and north-central U.S. and southeastern Canada. Bigtooth aspen is valuable for revegetating and improving disturbed sites. It also provides pulp for wood products and habitat and food for a variety of wildlife.
Light ![]()
Bigtooth aspen is very intolerant of shade and suckers from roots profusely. Because of these characteristics, clearcutting works best.
Water
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Bigtooth aspen is most often found on better soils of well-drained uplands. It rapidly colonizes exposed mineral soils.
Growth
![]()
Size
![]()
A medium sized tree with an irregular, thin crown and a straight bole.
Timber Value ![]()
Bigtooth aspen is used for pulp, particle board, structural panels, pallets, boxes, chop sticks, hockey stick components, ladders, and pelletized fuel.
Wildlife Value ![]()
Moose and deer browse stems and foliage. Beavers eat bark, leaves, twigs, branches. Ruffed grouse eat leaves, flower buds, and catkins.
Attracts moose, deer, beaver, grouse
Fun Facts
A pioneer species, bigtooth aspen produces an abundance of seeds. A single tree may produce more than 1.5 million lightweight seeds. Wind dispersal sends the cottony seeds great distances. It often exists in nearly pure stands following disturbances such as fire and heavy cutting.
Latin Meaning
Populus: Latin name /
grandidentata: with large teeth
Home - I.D. Fact Sheet - USDA Silvics Manual - Additional Silvics
Landowner Factsheets © 2004 Virginia Tech Forestry Department, all rights reserved. Text, images, and programming by: Dr. Jeff Kirwan, Dr. John R. Seiler, John A. Peterson, Edward C. Jensen, Guy Phillips, or Andrew S. Meeks.