Virginia Tech Dendrology
Virginia Tech Dendrology
red maple Aceraceae Acer
rubrum L.
![]()
![]()
![]() symbol: ACRU
symbol: ACRU
Leaf: Opposite, simple, 3 to 5 palmate lobes with serrated margin, sinuses relatively shallow (but highly variable), 2 to 4 inches long; green above, whitened and sometimes glaucous or hairy beneath.
Flower: Attractive but small, occur in hanging clusters, usually bright red but occasionally yellow, appear in early spring, usually before leaves.
Fruit: Clusters of 1/2 to 3/4 inch long samaras with slighly divergent wings, on long slender stems. Light brown and often reddish, ripen in late spring and early summer.
Twig: Reddish and lustrous with small lenticels, buds usually blunt, green or reddish (fall and winter) with several loose scales usually present, leaf scars V-shaped, 3 bundle scars, lateral buds slightly stalked, may be collateral buds present.
Bark: On young trees, smooth and light gray, with age becomes darker and breaks up into long, fine scaly plates.
Form: Medium sized tree up to 90 feet. In forest, trunk usually clear for some distance, in the open the trunk is shorter and the crown rounded.
Looks like: silver maple
- Norway maple
- mapleleaf viburnum
- sugar maple
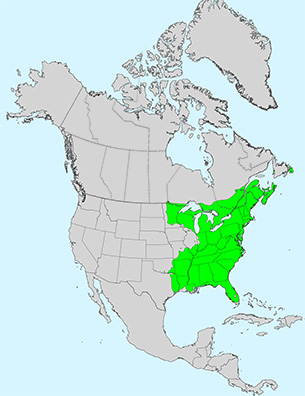
Additional Range Information: Acer rubrum is native to North America. Range may be expanded by planting. Download the full-size PDF map.
More Information: Fall Color - Wood
External Links: USDAFS Silvics of North America - USDAFS FEIS Silvics - USDA Plants Database - Horticulture Information - USDAFS Forest Products Lab
All material 2021 Virginia Tech Dept. of Forest Resources and Environmental Conservation; Photos and text by: John Seiler, Edward Jensen, Alex Niemiera, and John Peterson; Silvics reprinted from Ag Handbook 654; range map source information