Virginia Tech Dendrology
Virginia Tech Dendrology
white fir Pinaceae Abies
concolor (Gord. & Glend.) Lindl. ex Hildebr.
![]()
![]()
![]() symbol: ABCO
symbol: ABCO
Leaf: Flattened needles, silvery blue-green both above and below, 2 to 3 inches long, blunt at the tip, extending at right angles from the twig, often curving upwards. A citrus smell is present when the needle is broken. White bloom may be distributed evenly or may occur in distinct bands on both surfaces.
Flower: Species is monoecious; males yellow- to red-toned, catkin-like; females inconspicuous, yellow-brown.
Fruit: Cones are upright, 3 to 5 1/2 inches long, oblong, yellow-green to purple, with erose shoulders; deciduous at maturity with seed dispersal in fall.
Twig: Twigs are dark orange at first, becoming gray-green, then gray. Leaf scars are circular.
Bark: Thin, smooth and gray on young trees, with resin pockets. On old trees, thick, ashy gray with deep, irregular furrows.
Form: Young trees are conical. Older trees develop a dome-like crown.
Looks like: Pacific silver fir
- noble fir
- subalpine fir
- California red fir
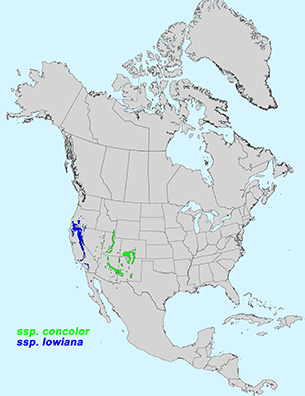
Additional Range Information: Abies concolor is native to North America. Range may be expanded by planting. Download the full-size PDF map.
More Information: Wood - Landowner Factsheet
External Links: USDAFS Silvics of North America - USDAFS FEIS Silvics - USDA Plants Database - Horticulture Information - USDAFS Forest Products Lab
All material 2025 Virginia Tech Dept. of Forest Resources and Environmental Conservation; Photos and text by: John Seiler, Edward Jensen, Alex Niemiera, and John Peterson; Silvics reprinted from Ag Handbook 654; range map source information