Virginia Tech Dendrology
Virginia Tech Dendrology
California red fir Pinaceae Abies
magnifica A. Murray bis
![]()
![]() symbol: ABMA
symbol: ABMA
Leaf: Flattened needles, about 1 inch long, linear, and 4-angled in cross-section with a ridge on top along the midrib; bluish white bloom on all surfaces; base curves, making the needle resemble a hockey stick; tips mostly rounded but may be pointed on cone-bearing branches; spirally arranged but usually upswept.
Flower: Species is monoecious; male cones purple to dark red and borne on undersides of branches; female cones are reddish-brown and borne upright near the top of the crown.
Fruit: Cones are 6 to 9 inches long, cylindrical, and borne upright on the twig; cone scales are deciduous, falling from the cone as seeds ripen; purple when mature; bracts are shorter than the scales (as opposed to noble fir). Shasta red fir (a hybrid) has bracts longer than cone scales.
Twig: Stiff, reddish brown, and covered with round, flat leaf scars when needles fall. Buds are small, rounded, brown and mostly non-resinous; terminal buds usually occur in clusters of three or more.
Bark: When young ashy white, later turning dark reddish brown and becoming deeply ridged and furrowed; inner bark a dark reddish brown.
Form: A large evergreen, 125 to 200 feet tall and 2 to 5 feet in diameter.
Looks like: white fir
- noble fir
- subalpine fir
- Pacific silver fir
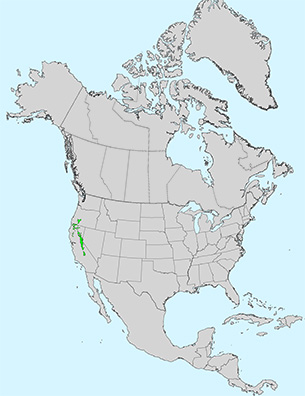
Additional Range Information: Abies magnifica is native to North America. Range may be expanded by planting. Download the full-size PDF map.
External Links: USDAFS Silvics of North America - USDAFS FEIS Silvics - USDA Plants Database
All material 2021 Virginia Tech Dept. of Forest Resources and Environmental Conservation; Photos and text by: John Seiler, Edward Jensen, Alex Niemiera, and John Peterson; Silvics reprinted from Ag Handbook 654; range map source information