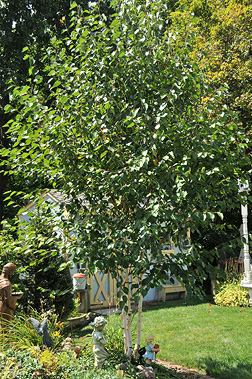Virginia Tech Dendrology
Virginia Tech Dendrology
Himalayan white birch Betulaceae Betula
utilis D. Don
![]()
![]() symbol:
symbol:
Leaf: Alternate, simple, pinnately–veined, ovate, 2 1/2 to 3 1/2 inches long, singly serrated to faintly doubly serrated, rounded to obtuse leaf base, dark green above and paler below.
Flower: Species is monoecious; 2 to 3, red brown, 1 to 1 1/2 inch long, preformed male catkins at the ends of twigs; females are upright, reddish green, 1 inch long; appear or elongate (males) in mid-spring.
Fruit: Cone like, cylindrical, 1 1/2 to 2 inches long, initially green but brown and deciduous when mature, breaking up to release small 2-winged nutlets; mature in autumn and disperse through winter.
Twig: Slender, red brown, light lenticels, may have a fine grey fuzz; buds are slender, pointed and red brown, false end bud.
Bark: Red brown with numerous horizontal lenticels when young; heavily peeling to a striking, creamy white (slight reddish) when mature.
Form: A small to medium sized tree up to 60 feet tall, pyramidal crown.
Looks like: European weeping birch
- paper birch
- gray birch
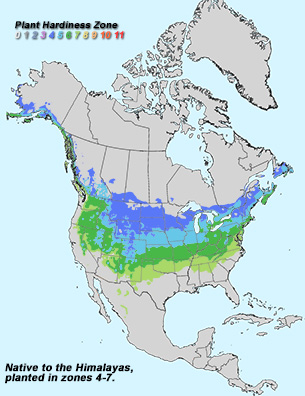
Additional Range Information: Betula utilis is planted in the USDA hardiness zones shown above and is not known to widely escape cultivaton. Download the full-size PDF map.
External Links:
All material 2025 Virginia Tech Dept. of Forest Resources and Environmental Conservation; Photos and text by: John Seiler, Edward Jensen, Alex Niemiera, and John Peterson; Silvics reprinted from Ag Handbook 654; range map source information