Virginia Tech Dendrology
Virginia Tech Dendrology
silver maple Aceraceae Acer
saccharinum L.
![]()
![]() symbol: ACSA2
symbol: ACSA2
Leaf: Opposite, simple with 5 deeply palmate sinuses, lobe margins coarsely serrate, 2 1/2 to 5 inches long; light green above, pale, silvery white below.
Flower: Species is monoecious; greenish to reddish flowers appear in dense clusters in early spring long before leaves.
Fruit: Samara, largest of any native maple, divergent wings 1 1/2 to 2 1/2 inches long, germinate as soon as released, mature in late spring.
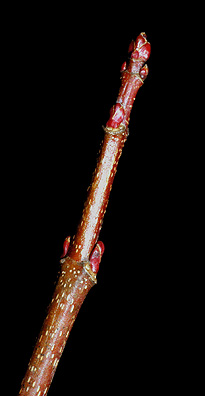
Twig: Similar to red maple but stouter and often more chestnut-brown in color, unpleasant odor when crushed; buds reddish brown with large scales, flower buds often in conspicuous dense clusters.
Bark: Light gray and smooth when young, when older breaks up into long thin strips, loose at ends. Similar to red maple but coarser.
Form: Can become quite a large tree reaching over 100 feet tall, trunk usually short, dividing into several subtrunks. Long slender branches sweep downward and then curve gracefully upwards.
Looks like: red maple
- sugar maple
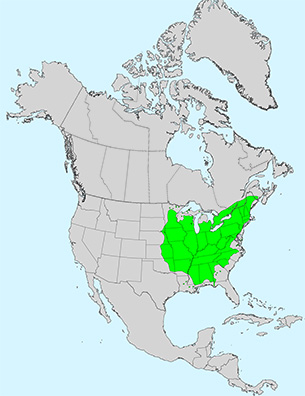
Additional Range Information: Acer saccharinum is native to North America. Range may be expanded by planting. Download the full-size PDF map.
More Information: Fall Color - Wood
External Links: USDAFS Silvics of North America - USDAFS FEIS Silvics - USDA Plants Database - Horticulture Information - USDAFS Forest Products Lab
All material 2021 Virginia Tech Dept. of Forest Resources and Environmental Conservation; Photos and text by: John Seiler, Edward Jensen, Alex Niemiera, and John Peterson; Silvics reprinted from Ag Handbook 654; range map source information