Virginia Tech Dendrology
Virginia Tech Dendrology
Pacific yew Taxaceae Taxus
brevifolia Nutt.
![]()
![]() symbol: TABR2
symbol: TABR2
Leaf: Evergreen needles, single, spirally arranged (although they appear 2-ranked), 1 inch long, yellow-green to dark green above and paler below (but without bloom); apex pointed but not sharp; each needle has a distinct petiole that parallels the twig for a short distance.
Flower: Species is dioecious; male flowers are small, round, and yellow and are borne on the undersides of the leaves; female flowers are solitary.
Fruit: A round, fleshy, orange-red aril about 1/4 inch long containing one hard seed, exposed at the end.
Twig: Round, slender, and remaining green for many years; relatively few lateral branches.
Bark: Always thin (about 1/4 inch), reddish brown, and scaly; inner bark is reddish purple.
Form: Small evergreen understory tree with indistinct growth form. Can reach 50 feet tall and 2 feet in diameter, but usually much smaller. Trunks are usually fluted and asymmetrical. Very slow growing but can reach a very old age.
Looks like: English yew
- Japanese yew
- Anglo-Jap yew
- western hemlock
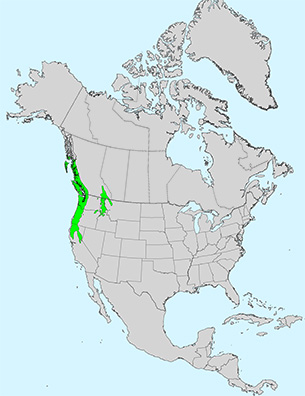
Additional Range Information: Taxus brevifolia is native to North America. Range may be expanded by planting. Download the full-size PDF map.
External Links: USDAFS Silvics of North America - USDAFS FEIS Silvics - USDA Plants Database - USDAFS Forest Products Lab
All material 2025 Virginia Tech Dept. of Forest Resources and Environmental Conservation; Photos and text by: John Seiler, Edward Jensen, Alex Niemiera, and John Peterson; Silvics reprinted from Ag Handbook 654; range map source information