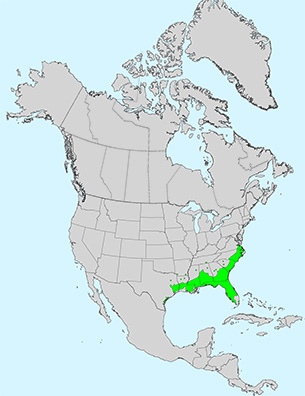


A bottomland tree of the southeast that is sometimes planted as an ornamental.
Light ![]()
Laurel oak is considered invasive, and it will replace pine in the absence of fire.
Water
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
A bottomland tree found in wetlands and along streams. It will grow well in uplands when planted there.
Growth
![]()
Size
![]()
Medium size tree to 60 feet, straight trunk, 1 to 3 feet in diameter, rounded crown.
Timber Value ![]()
Laurel oak is used for lumber, veneer for plywood used in making fruit and vegetable boxes, and fuelwood.
Wildlife Value ![]()
Laurel oak produces regular large crops of acorns, making it an important food source.
Attracts deer, raccoon, birds, rodents
Fun Facts
Confusion abounds between this tree and Quercus hemisphaerica and some authors do not separate the two. Laurel oak is a very fast growing tree but relatively short-lived. It is also called swamp laurel oak.
Latin Meaning
Quercus: Latin name /
laurifolia: laurel-like leaves
Home - I.D. Fact Sheet - USDA Silvics Manual - Additional Silvics
Landowner Factsheets © 2004 Virginia Tech Forestry Department, all rights reserved. Text, images, and programming by: Dr. Jeff Kirwan, Dr. John R. Seiler, John A. Peterson, Edward C. Jensen, Guy Phillips, or Andrew S. Meeks.