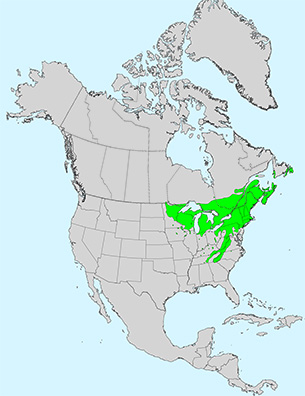



Yellow birch is the most useful of North American birches, appreciated for its wood quality, its ability to provide wildlife with sustenance, and its attractive, pale golden, exfoliating bark.
Light ![]()
Due to moderate shade tolerance, less than that of common associates (sugar maple, American beech, and hemlock), yellow birch requires methods that allow for ample light to reach the forest floor. Shelterwoods and patch clearcuts are suitable.
Water
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Yellow birch is considered a gap species that develops best on sandy loam soils. In the southern portion of its range, yellow birch occurs in cool, moist locations.
Growth
![]()
Size
![]()
A medium size tree to 75 feet with an irregular crown.
Timber Value ![]()
Yellow birch is used for lumber, veneer, paneling, plywood, cabinets, boxes, interior doors. It is also used in the distillation of wood alcohol, acetate of lime, charcoal, tar, and oils.
Wildlife Value ![]()
Important browse plant for moose and deer. Many other species feed on seeds, catkins, buds, and sap.
Attracts red squirrels, porcupines, songbirds, grouse snowshoe hares, deer, moose
Fun Facts
Yellow birch wood is used for furniture and veneer. The bark peels are flammable, and can be used to start a fire - even when wet. Seeds often germinate on stumps, which later rot away leaving a tree supported by "stilts".
Latin Meaning
Betula: Latin (pitch - bitumen is distilled from the bark or Sanskrit "bhurja" (to shine" (bark))) /
alleghaniensis: of the Alleghany region
Home - I.D. Fact Sheet - USDA Silvics Manual - Additional Silvics
Landowner Factsheets © 2004 Virginia Tech Forestry Department, all rights reserved. Text, images, and programming by: Dr. Jeff Kirwan, Dr. John R. Seiler, John A. Peterson, Edward C. Jensen, Guy Phillips, or Andrew S. Meeks.