white oak Fagaceae Quercus alba
Leaf:Alternate, simple, oblong to ovate in shape, 4 to 7 inches long; 7 to 10 rounded, finger-like lobes, sinus depth varies from deep to shallow, apex is rounded and the base is wedge-shaped, green to blue-green above and whitish below.
Flower:Species is monoecious; male flowers are yellow-green, borne in naked, slender catkins, 2 to 4 inches long; female flowers are reddish green and appear as very small single spikes; appearing with the leaves in mid-spring.
Fruit:Ovoid to oblong acorn, cap is warty and bowl-shaped, covers 1/4 of the fruit; cap always detaches at maturity; matures in one growing season in the early fall.
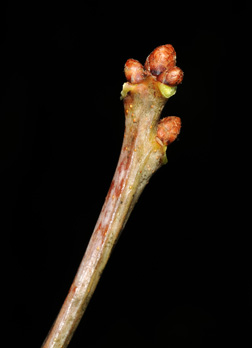
Twig:Red-brown to somewhat gray, even a bit purple at times, hairless and often shiny; multiple terminal buds are red-brown, small, rounded (globose) and hairless.
Bark:Whitish or ashy gray, varying from scaly on smaller stems to irregularly platy or blocky on large stems. On older trees smooth patches are not uncommon.
Form:A very large tree; when open grown, white oaks have rugged, irregular crowns that are wide spreading, with a stocky bole. In the forest crowns are upright and oval with trees reaching up to 100 feet tall and several feet in diameter.





Notes: