

Red alder is the most common and most useful deciduous tree along coastal portions of the Pacific northwest. Due to nitrogen fixing abilities and speedy juvenile growth, red alder is potentially valuable for crop rotation systems and reclamation and improvement of infertile land.
Light ![]()
Red alder is shade intolerant and needs full sun for regeneration. A pioneer species, red alder is favored by disturbances such as fire and logging. Traditionally, red alder growth is discouraged in favor of more valued western conifer timber sources.
Water
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
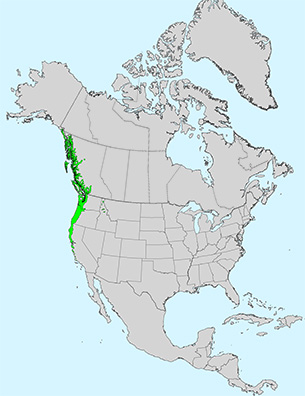
Occurs along streams, bottomlands, and on moist mountain slopes where soil is disturbed, ranges from southeastern Alaska to southern California, primarily on the west side of the Cascades and Sierras. Ranges in elevation from sea level to 3500 feet.
Growth
![]()
Size
![]()
A medium sized tree reaching 120 feet tall and 1 to 3 feet in diameter. Typically has a moderately straight bole with an open, broadly pyramidal or dome-shaped crown. Lower trunk is usually free of branches due to intolerance to shade.
Timber Value ![]()
Red alder is used for furniture, cabinets, trim, paneling, plywood, pallets, veneer, writing paper, tissue paper, paper roll plugs, etc.
Wildlife Value ![]()
Deer and elk eat the twigs, buds, leaves. Beavers eat the bark and use the wood for dams and lodges. Many birds and rodents eat the seeds.
Attracts deer mice, beaver, deer, elk, redpolls, siskins, goldfinches
Fun Facts
Red alder is the largest of all the alders and the most abundant hardwood in the U.S. northwest. Intolerant of shade and understory conditions, often forms relatively pure even-aged stands. Wood is used for furniture, wooden utensils, and a variety of minor manufactured products. Red alder coals are used to smoke salmon. In Oregon, reforestation with red alder requires permission from the OR Dept. of Forestry. Important nitrogen-fixing plant.
Latin Meaning
Alnus: Latin name for alder /
rubra: red
Home - I.D. Fact Sheet - USDA Silvics Manual - Additional Silvics
Landowner Factsheets © 2004 Virginia Tech Forestry Department, all rights reserved. Text, images, and programming by: Dr. Jeff Kirwan, Dr. John R. Seiler, John A. Peterson, Edward C. Jensen, Guy Phillips, or Andrew S. Meeks.