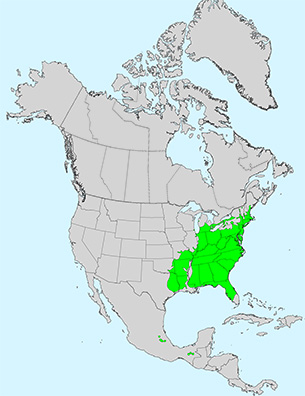
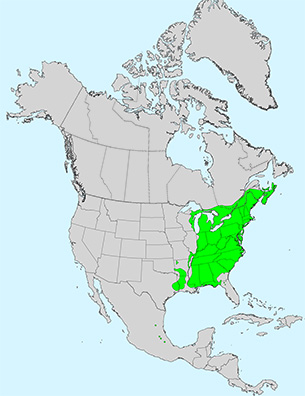
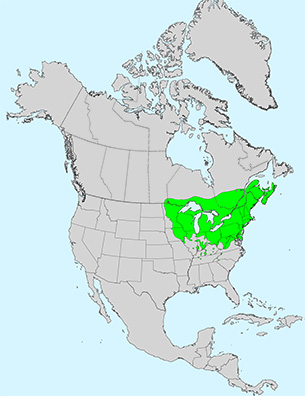
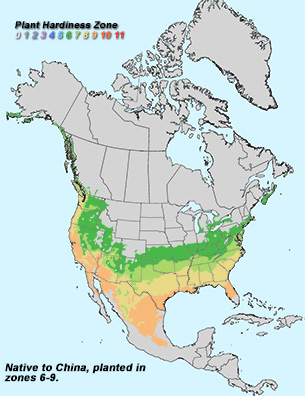
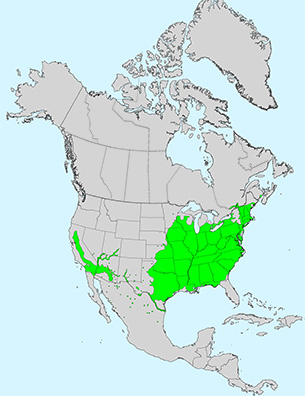
Leaf: Opposite, pinnately compound, 3 to 5 leaflets (sometimes 7), 2 to 4 inches long, margin coarsely serrate or somewhat lobed, shape variable but leaflets often resemble a classic maple leaf, light green above and paler below.
Flower: Species is dioecious; yellow-green, in drooping racemes; appearing in spring.
Fruit: Paired V-shaped samaras, 1 to 1 1/2 inches long, in drooping clusters,light tan when ripe in fall, persist throughout winter.
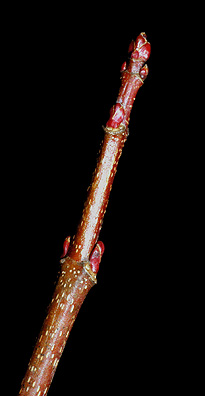
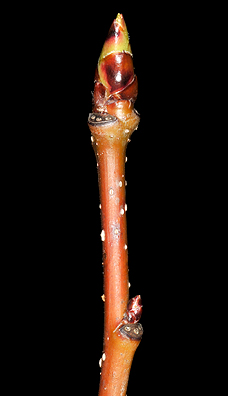
Twig: Green to purplish green, moderately stout, leaf scars narrow, meeting in raised points, often covered with a glaucous bloom; buds white and hairy, lateral buds appressed.
Bark: Thin, gray to light brown, with shallow interlacing ridges; young bark is generally warty.
Form: Medium sized tree to 60 feet, typically with poor form and multiple trunks; sprouts often occur on bole.






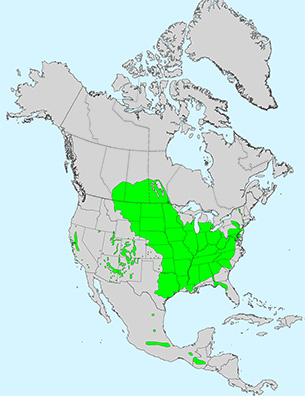
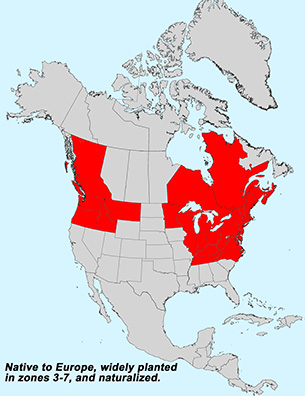
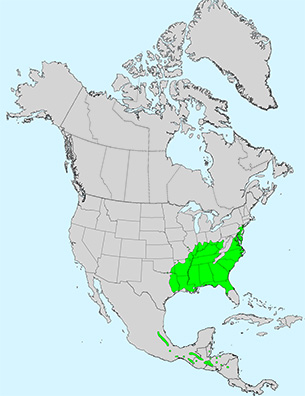
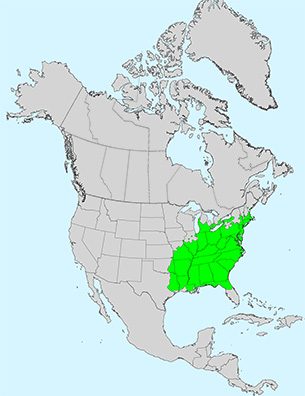
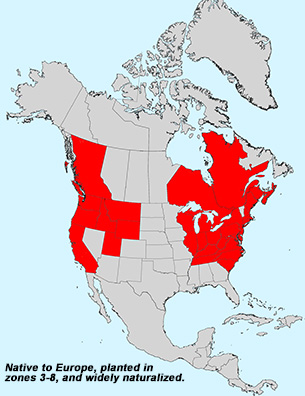
Notes: